Sales enablement is the joint revenue responsibility between sales and marketing. The concept of a shared approach started to gain traction in the early 2000's. Today it has evolved from a basic alignment to reaching strategic levels of organizational sales enablement adoption rates of 33%. As the most urgent initiative for B2B sales success, organizations need a framework of best practices to effectively define, execute and sustain sales enablement practices.
.jpg?width=622&height=325&name=1200x627%20(15).jpg)
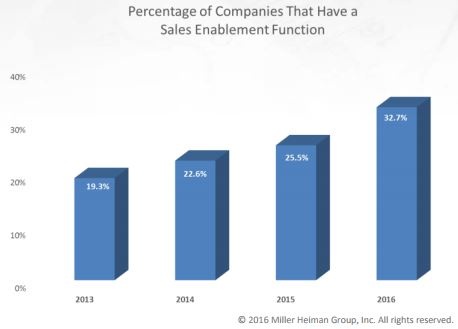
Sales enablement adoption was up 33% in 2016, but many organizations are still navigating through which practices to implement. At the same time, companies with sales enablement functions are increasing win rates by 9% up to 50.5% and decreasing ramp-up time by at least 30-40%.
The success of sales enablement programs depends on top down support and highly aligned execution, analysis and flexibility to make adjustments accordingly. When planning a new program or streamlining existing sales enablement functions, this list of top best practices will guide you through the process.
5 best practices for B2B sales enablement
- Make the practice part of your company culture Buy-in from the top is critical for sustainable impact. Top down support ensures the traction needed for a well-functioning sales and marketing machine. Sales effectiveness research shows that 72% of top performing sales organizations report having strong or outstanding teamwork already in place. Communication from the top gives the credibility and authority to push the program forward and spread throughout to the rest of the organization.
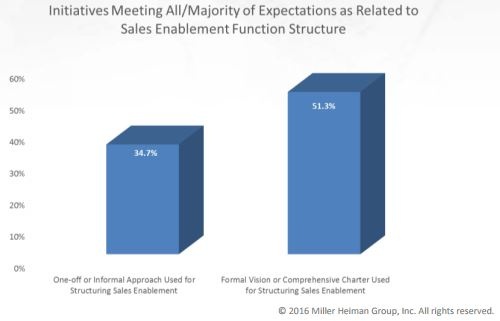
- Formalize the program to be systematic 16.6% more organizations with a formal vision or charter for sales enablment (vision, services, road-map, and success metrics) meeet all or the majority of expectations over those that take a one-off or informal approach.
- Ownership identify who owns sales enablement initiatives. Some will argue sales, while other say it's a joint effort, and others defend that it sits within marketing. Ultimately the owner or owners need to agree on the final goal-- to generate revenue (sales-minded) in the most effective way (marketing-minded). Sales operation traditionally took the lead in sales enablement, but the execution tends to be reactive or administrative. In practice sales is concerned with meeting aggressive targets. While marketing It has grown into an active role in nurturing a lead through the sales funnel. The sales process today is buyer-led. Whether the role is centralized in the head of sales enablement or shared by a multi-profile team is up to each organization and the influence, authority, and support the role has within the company.
- Sales journey definition The customer journey includes buyer personas, path and delegating responsibilities between sales and marketing. . when the buyer wants to leverage these resources. B2B sales cycles need sales enablement mechanisms to touch people at every stage of fluctuating buyer journeys. A potential client can spend a few minutes or months searching online for a solution. They then enter your web page jumping from the "about" page to the product page to free demo then to pricing. In between online interactions, a lead completes a contact form which a sales rep then qualifies offline. Content needs to be available and reach potential leads looking to discover products on their own, while sales collateral and processes support client-facing interactions.
 .
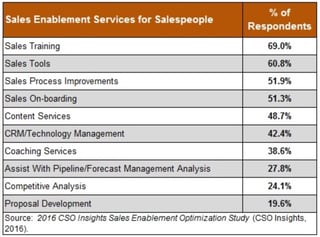
. - What sales need Content creators produce and make the content available to sales to present to clients. Best practices, research, and tools can be generated through a cross-functional sales-marketing team that sales will use internally. The tools and content need to be easy to access, consume and reusable across the sales organization. Anything that improves sales from sales collateral to forecasting falls under the sales enablement umbrella. The most commonly used strategies include pipeline management, technology integration, account-based marketing, content accessibility, establishing closed-loop analytics to determine the effectiveness of sales collateral and onboarding/training for sales staff. Find opportunities for real use cases and feedback on use of sales collateral. Common resource requirements include content, conversation guides, and sales training.
- Alignment and accountability It’s not uncommon to hear that sales never follows up on marketing leads or that marketing sends over poor quality leads. Sales enablement research shows that 60% of best-in-class marketing teams have deep insights into sales, and 73% of best-in-class sales teams have insight into marketing activities. Marketing is in charge of creating and training while sales management makes sure that the sales enablement program is put into practice. Sales enablement is a great opportunity for marketing to actively support the sales funnel with content, customer insights and stories from real client interactions. It is perfectly suited for marketing to own that, and create consistency to speed up customer conversations. With marketing and sales roles defined stakeholders must reach an agreement on shared revenue goals, who a good-fit customer is and why defined for each stage of sales process.

- Training Marketing is usually responsible for creating the vast majority of the content and bears most of the responsibility for training the sales organization. Sessions on how to use the resources provided, discuss real scenarios and include role playing. Sales operations takes on the crucial role of “operationalizing” the information sales receives from the sales enablement team. Training and development is an important part of most programs to ensure optimal execution. The most effective programs conduct traditional training programs, but also use technologies like collaboration tools to make sales training continuous.
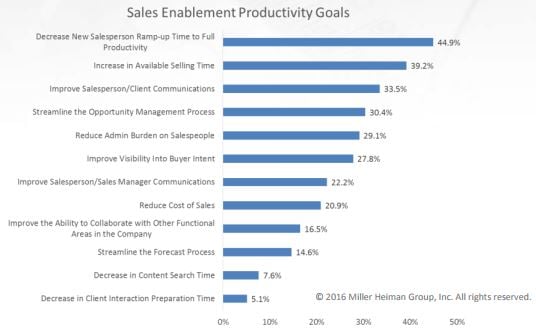
- Monitor, measure and adjust Once tools and content are made available, monitor and track usage to make necessary adjustments. Track and enforce whether resources are being used across the sales organization. The head or team of sales enablement leads periodic meetings with sales reps for offline feedback. Set productivity goals to measure successes and track areas of improvement. Eliminate fluff, modify existing content to match KPIs and what sales reps are finding in the field. Knowing what works and what doesn't is key to sales acceleration and the success of the program. Meaningful sales enablement metrics that you should track include: average sales cycle length; number of reps achieving quota; and average deal size.
Use these best practices to set up the frameworks needed for a successful B2B sales enablement program that fit within your own corporate culture.




-1.jpg)
.jpg)

